Color theory serves as the scientific foundation for creating visually compelling apparel collections. At Ludyway, we recognize color as a strategic business tool that influences consumer perception and brand identity. This comprehensive guide explores professional color application methodologies for fashion designers and brands.

Color Theory Fundamentals
Color theory comprises principles governing color mixing and visual effects. Sir Isaac Newton’s 1666 color circle established the foundation for modern color systems. Understanding these mechanics enables designers to:
- Create cohesive seasonal collections
- Enhance product appeal through strategic color combinations
- Develop distinctive brand identities
Contemporary fashion applications utilize both subtractive (pigment-based) and additive (light-based) color models to achieve precise results across different media and materials.
The Color Wheel Framework

Primary Color Systems
Different production methods utilize distinct primary systems:
| System | Primary Colors | Fashion Applications |
|---|---|---|
| RYB | Red, Yellow, Blue | Traditional textile dyeing, hand-painted fabrics |
| RGB | Red, Green, Blue | Digital design, e-commerce displays, virtual prototyping |
| CMYK | Cyan, Magenta, Yellow, Black | Commercial printing, pattern transfers, sublimation |
Secondary and Tertiary Colors
Secondary colors (orange, green, purple) emerge from primary combinations. Tertiary colors result from mixing primary and secondary hues, creating sophisticated transitional shades essential for gradient designs and complex patterns.
Color Properties: HSV Model

The Hue-Saturation-Value system provides precise color control:
- Hue: Base pigment position on color wheel
- Saturation: Color intensity (0% = grayscale, 100% = maximum vibrancy)
- Value: Lightness/darkness (0% = black, 100% = white)
Professional designers manipulate these parameters to create cohesive seasonal palettes with balanced visual weight.
Color Production Systems
RGB: Digital Color Creation
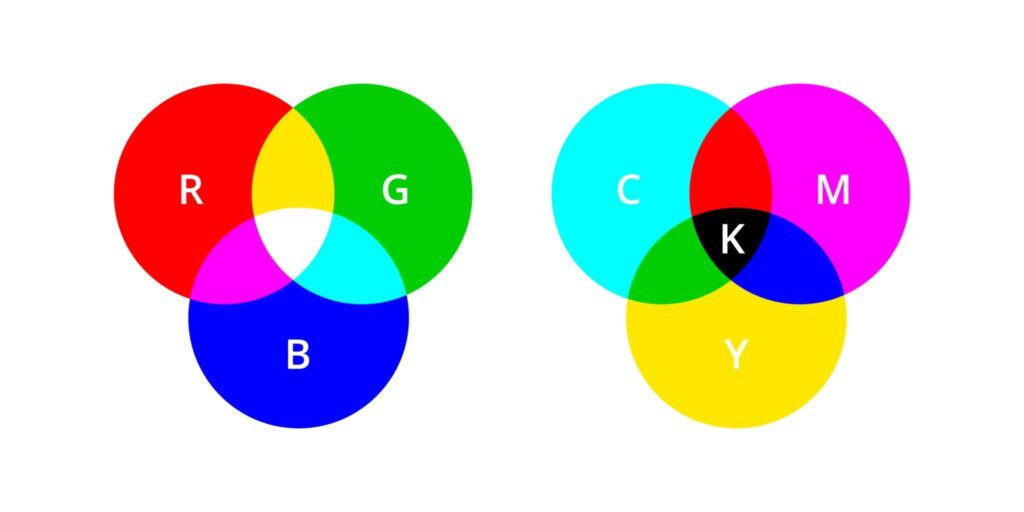
The additive RGB model combines light wavelengths to create colors. Critical applications include:
- E-commerce product visualization
- Digital textile printing preparation
- Virtual garment prototyping
RGB’s wide gamut enables vibrant digital representations but requires conversion to CMYK or Pantone for physical production.
CMYK: Physical Production Standard
The subtractive CMYK model forms the foundation for physical apparel production. Key considerations:
- Four-color process printing limitations
- Spot color matching with Pantone systems
- Material-specific color absorption variations
At Ludyway, our custom cut and sew services incorporate advanced color matching technologies to maintain consistency across production runs.
Advanced Color Terminology

Professional color vocabulary ensures precise specification:
| Term | Definition | Production Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Shade | Hue + Black | Increases depth perception |
| Tint | Hue + White | Creates pastel variations |
| Tone | Hue + Gray | Produces sophisticated muted colors |
Mastering these variations enables nuanced collection development across different garment types, from custom t-shirts to technical outerwear.
Professional Color Schemes

Monochromatic Schemes
Utilizes variations of a single hue through tints, tones, and shades. Benefits include:
- Streamlined production color management
- Cohesive visual merchandising
- Reduced manufacturing complexity
Particularly effective for capsule collections and uniform programs, including custom uniform manufacturing.
Complementary Color Systems

Pairs opposite colors on the wheel for maximum contrast. Implementation strategies:
- 80/20 dominance principle (primary/secondary color ratio)
- Strategic placement in high-impact areas
- Balancing warm and cool undertones
Highly effective in custom sports apparel where visibility and brand recognition are paramount.
Split-Complementary Systems
Uses a base color with two adjacent complementary hues. Advantages:
- Enhanced harmony compared to straight complementary
- Greater design flexibility
- Reduced visual tension
Requires careful value balancing to maintain cohesion across product lines.
Analogous Color Schemes
Combines 3-5 adjacent colors on the wheel. Professional implementation follows:
- 60% dominant color: Main collection pieces
- 30% secondary color: Complementary items
- 10% accent color: Detail elements and trim
Creates sophisticated tonal collections with natural visual progression.
Triadic Color Structures
Uses three evenly spaced colors for vibrant, balanced palettes. Best practices:
- Designate one color as dominant
- Use others for strategic accents
- Maintain consistent saturation levels
Particularly effective for youth-oriented collections and custom hoodies where energy and vibrancy are key.
Tetradic Color Systems
Employs two complementary pairs for complex palettes. Implementation guidelines:
- Establish clear visual hierarchy
- Balance warm and cool tones
- Use neutral bases to ground vibrant combinations
Requires advanced technical execution to maintain production consistency across multiple colors.
Industry Applications
Seasonal Palette Development
Professional color forecasting incorporates:
- Market trend analysis
- Historical sales data
- Cultural influences
- Material availability
Ludyway’s manufacturing expertise helps brands translate palettes into production-ready specifications.
Technical Implementation
Accurate color reproduction requires:
- Standardized lighting conditions for approval
- Digital color matching systems
- Batch consistency protocols
- Material-specific dyeing techniques
Professional Practice
Three-Color Rule
The industry-standard guideline for visual cohesion:
- Primary color: 60% of collection
- Secondary color: 30%
- Accent color: 10%
Neutrals (black, white, gray) function as structural elements outside this system.
Color Psychology in Fashion
Strategic color selection influences consumer response:
| Color Family | Psychological Impact | Common Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Blues | Trust, stability | Corporate wear, uniforms |
| Reds | Energy, urgency | Sale items, performance wear |
| Greens | Natural, sustainable | Eco-collections, outdoor gear |
Conclusion
Mastering color theory provides fashion brands with a significant competitive advantage. By understanding color relationships, production systems, and psychological impacts, designers can create cohesive collections that resonate with target audiences. Implementation requires technical expertise in color matching and production consistency – areas where Ludyway’s manufacturing capabilities deliver exceptional results across all apparel categories.
As global fashion manufacturing partners, we transform color concepts into production-ready specifications while maintaining quality standards from initial sampling through bulk production. Contact our team to discuss your next collection’s color strategy and manufacturing requirements.













